

In couple of my designs I have used voltage references. I thought to write up a blog on Bandgap voltage reference in such a way that it may be effectual for professionals and understandable to novice designers.
Voltage reference is an electronic device (circuit or component) that produces a fixed (constant) voltage irrespective of the loading on the device, power supply variation and temperature.
Reference voltages and/or currents with little dependence to temperature prove useful in many analog circuits.
As many process parameters vary with temperature, if a reference is temperature-independent, it is usually process independent, as well.
If two quantities with opposite temperature coefficient are added with proper weighting, the resultant quantity theoretically exhibits zero temperature coefficient.
For V1 and V2 with opposite temperature dependence, the coefficients c1 and c2 can be chosen in such a way that
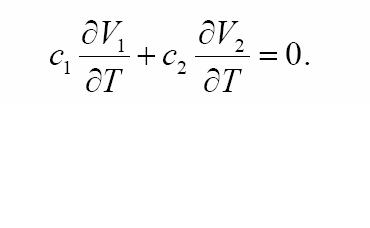
Among various devices in the semiconductor technology, the characteristics of the bipolar transistors have proven the most reproducible and well-defined quantities that provide positive and negative temperature coefficients.
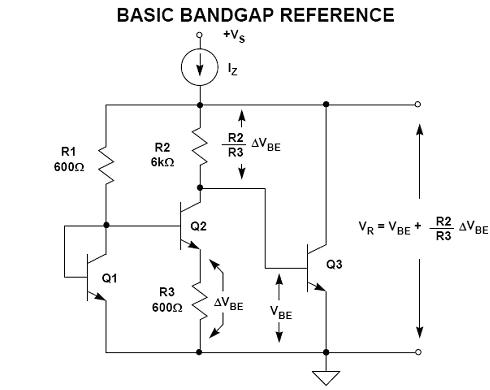
Bandgap Voltage Reference
• The most popular technique for both Bipolar and CMOS technologies.
• Generates a fixed dc reference voltage that does not change with temperature.
• Cancels the negative temperature dependence of a PN junction with positive temperature dependence from a PTAT (proportional-to-absolute-temperature) circuit.
The term with negative temperature dependence is the forward-biased voltage of a diode (usually base-emitter junction). The PTAT term is realized by amplifying the voltage difference of two forward-biased diodes ( i.e., base-emitter junctions).
# 1
Ajay Kumar Yadav October 20,2008 - 3:15pm |
# 2
Art Gray October 20,2008 - 3:45pm |
# 3
Mark Thomson October 20,2008 - 3:59pm |
# 4
Sanjay Chawla October 20,2008 - 4:35pm |